
Depreciation, in financial terms, represents the allocation of the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life. It's a crucial concept for understanding a company's financial health and accurately reflecting its assets' true value over time. Think of it this way: you buy a car. It's brand new, but every year its value decreases due to wear and tear, obsolescence, and simply being a year older. Depreciation accounts for this decline in value.
Why is depreciation important? Firstly, it's a matching principle requirement under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). This principle dictates that expenses should be recognized in the same period as the revenues they help generate. By expensing a portion of an asset's cost over its useful life, depreciation helps match the cost of the asset with the revenue it generates during that time. Without depreciation, the entire cost would be expensed in the year of purchase, artificially lowering profits in that year and overstating them in subsequent years.
Secondly, depreciation provides a more accurate picture of a company's profitability. It helps to smooth out earnings over time, presenting a more consistent and realistic view of performance. This is beneficial for investors and stakeholders who rely on financial statements to make informed decisions.
There are several methods for calculating depreciation, each with its own nuances. Some of the most common include:
- Straight-Line Depreciation: This is the simplest method, where the asset depreciates by the same amount each year. The formula is (Cost - Salvage Value) / Useful Life. Salvage value is the estimated value of the asset at the end of its useful life.
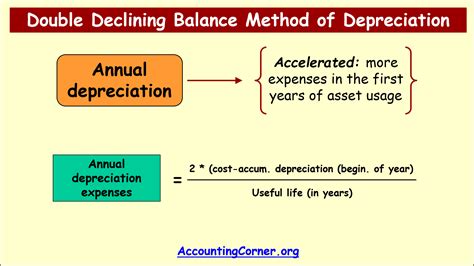
- Double-Declining Balance: This is an accelerated depreciation method that results in higher depreciation expense in the early years of the asset's life and lower expense later on. It's calculated as 2 * (Straight-Line Depreciation Rate) * Book Value. Book value is the asset's cost less accumulated depreciation.
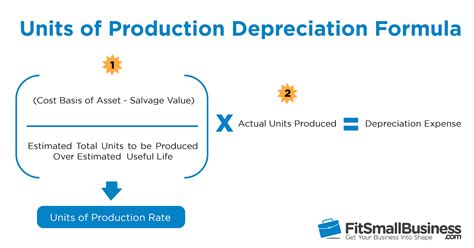
- Units of Production: This method depreciates the asset based on its actual usage or output. The depreciation expense is calculated based on the actual units produced or service provided relative to the total estimated units or service the asset can provide.
The choice of depreciation method can significantly impact a company's reported earnings and tax liability. Companies often choose a method that aligns with their specific industry and asset type. For example, a manufacturing company with heavy machinery might use an accelerated method to reflect the faster rate of wear and tear.
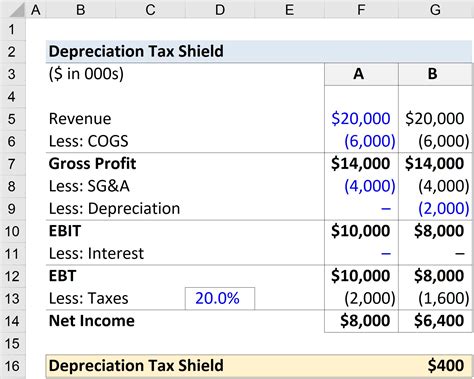
It's important to note that depreciation is a non-cash expense. While it reduces net income, it doesn't involve an actual outflow of cash. This is why depreciation is often added back to net income when calculating cash flow from operations. This adjustment helps to determine the true cash-generating ability of the business.
In conclusion, depreciation is a vital accounting concept that reflects the decline in value of tangible assets over time. It ensures accurate financial reporting, matches expenses with revenues, and provides a more realistic view of a company's profitability. Understanding depreciation methods and their impact on financial statements is crucial for investors, analysts, and anyone seeking to assess a company's financial performance effectively.
 1200×900 accelerated depreciation electric vehicle charging settings sybil kristan from arleeqclarice.pages.dev
1200×900 accelerated depreciation electric vehicle charging settings sybil kristan from arleeqclarice.pages.dev
 2318×1502 bonus depreciation calculator nicky anabella from tracyyauguste.pages.dev
2318×1502 bonus depreciation calculator nicky anabella from tracyyauguste.pages.dev
 1500×1000 depreciation rate construction equipment yvette seo blog from storage.googleapis.com
1500×1000 depreciation rate construction equipment yvette seo blog from storage.googleapis.com
 3000×2000 depreciation calculated from tvasherbrooke.com
3000×2000 depreciation calculated from tvasherbrooke.com
 951×674 depreciation definition examples market business news from www.cnss.gov.lb
951×674 depreciation definition examples market business news from www.cnss.gov.lb
 961×697 depreciation rules nissa anallise from leabmerilyn.pages.dev
961×697 depreciation rules nissa anallise from leabmerilyn.pages.dev
 556×371 depreciation expense accounting methods dummies from www.dummies.com
556×371 depreciation expense accounting methods dummies from www.dummies.com
 0 x 0 calculate declining balance method depreciation from www.youtube.com
0 x 0 calculate declining balance method depreciation from www.youtube.com
 2002×1127 double declining balance method depreciation accounting corner from accountingcorner.org
2002×1127 double declining balance method depreciation accounting corner from accountingcorner.org
 1024×461 depreciation formula calculate depreciation expense from www.wallstreetmojo.com
1024×461 depreciation formula calculate depreciation expense from www.wallstreetmojo.com
 2048×1170 types depreciation from www.civilease.com
2048×1170 types depreciation from www.civilease.com
 1024×526 straight depreciation method accounting from www.online-accounting.net
1024×526 straight depreciation method accounting from www.online-accounting.net
 1200×1200 depreciation definition types purpose from moneysmint.com
1200×1200 depreciation definition types purpose from moneysmint.com
 1200×872 double declining balance method depreciation from www.careerprinciples.com
1200×872 double declining balance method depreciation from www.careerprinciples.com
 1497×2831 depreciation calculated quickbooks south africa from quickbooks.intuit.com
1497×2831 depreciation calculated quickbooks south africa from quickbooks.intuit.com
 1080×810 depreciation schedule template straight calculator diminishing from www.etsy.com
1080×810 depreciation schedule template straight calculator diminishing from www.etsy.com
 1024×768 depreciation recapture tax rate hatti koralle from marshawfarra.pages.dev
1024×768 depreciation recapture tax rate hatti koralle from marshawfarra.pages.dev
 900×500 bonus depreciation rates jess romola from kristiwnancy.pages.dev
900×500 bonus depreciation rates jess romola from kristiwnancy.pages.dev
 550×539 depreciation definition objectives methods business jargons from businessjargons.com
550×539 depreciation definition objectives methods business jargons from businessjargons.com
 3344×1878 asset depreciation introduction summary maximo secrets from maximosecrets.com
3344×1878 asset depreciation introduction summary maximo secrets from maximosecrets.com
 1500×1000 accumulation definition from ar.inspiredpencil.com
1500×1000 accumulation definition from ar.inspiredpencil.com
 1200×1200 currency depreciation appreciation definitions examples thestreet from www.thestreet.com
1200×1200 currency depreciation appreciation definitions examples thestreet from www.thestreet.com
 1197×675 depreciation calculate depreciation business from www.shiksha.com
1197×675 depreciation calculate depreciation business from www.shiksha.com
 1024×526 depreciation expenses formula examples excel template from www.educba.com
1024×526 depreciation expenses formula examples excel template from www.educba.com
 1536×458 depreciation meaning types calculation glossary from www.tickertape.in
1536×458 depreciation meaning types calculation glossary from www.tickertape.in
 1162×743 accumulated depreciation overview works from corporatefinanceinstitute.com
1162×743 accumulated depreciation overview works from corporatefinanceinstitute.com
 1280×720 depreciation rental property work eligibility from www.educba.com
1280×720 depreciation rental property work eligibility from www.educba.com
 800×450 depreciation methods check formula factors types especia from especia.co.in
800×450 depreciation methods check formula factors types especia from especia.co.in
 1024×526 accumulated depreciation assets falasislam from falasislam.weebly.com
1024×526 accumulated depreciation assets falasislam from falasislam.weebly.com
 945×787 financial accounting efinancemanagementcom from efinancemanagement.com
945×787 financial accounting efinancemanagementcom from efinancemanagement.com
 1500×1000 depreciation accumulated depreciation expense from ar.inspiredpencil.com
1500×1000 depreciation accumulated depreciation expense from ar.inspiredpencil.com
 1200×675 depreciation expense double entry bookkeeping from www.double-entry-bookkeeping.com
1200×675 depreciation expense double entry bookkeeping from www.double-entry-bookkeeping.com
 1772×2475 deduct rental property depreciation wealthfit from wealthfit.com
1772×2475 deduct rental property depreciation wealthfit from wealthfit.com
 900×500 calculate depreciation disposal fixed assets edward from storage.googleapis.com
900×500 calculate depreciation disposal fixed assets edward from storage.googleapis.com
 2500×1309 units production depreciation calculate formula from fitsmallbusiness.com
2500×1309 units production depreciation calculate formula from fitsmallbusiness.com
 1770×1418 bonus depreciation calculator cissy deloris from prudivfelecia.pages.dev
1770×1418 bonus depreciation calculator cissy deloris from prudivfelecia.pages.dev
 1280×720 depreciate heavy equipment elizabeth gunther blog from storage.googleapis.com
1280×720 depreciate heavy equipment elizabeth gunther blog from storage.googleapis.com
 768×435 depreciation gcse maths steps examples worksheet from thirdspacelearning.com
768×435 depreciation gcse maths steps examples worksheet from thirdspacelearning.com
 1280×720 funding resources mortgage corp maryleerenee from maryleerenee.blogspot.com
1280×720 funding resources mortgage corp maryleerenee from maryleerenee.blogspot.com
 625×404 double declining balance method definition meaning from www.myaccountingcourse.com
625×404 double declining balance method definition meaning from www.myaccountingcourse.com
 1920×1080 factors affect car depreciation rate indus from indususedcars.com
1920×1080 factors affect car depreciation rate indus from indususedcars.com
 3200×2400 ways account accumulated depreciation wikihow from www.wikihow.com
3200×2400 ways account accumulated depreciation wikihow from www.wikihow.com
 5465×3418 accumulated depreciation credit balance from www.investopedia.com
5465×3418 accumulated depreciation credit balance from www.investopedia.com
 1200×1552 chapter depreciation guide computation system level from nap.nationalacademies.org
1200×1552 chapter depreciation guide computation system level from nap.nationalacademies.org
 1280×719 depreciation expense debit credit financial falconet from financialfalconet.com
1280×719 depreciation expense debit credit financial falconet from financialfalconet.com
 3200×2400 ways calculate depreciation fixed assets wikihow from www.wikihow.com
3200×2400 ways calculate depreciation fixed assets wikihow from www.wikihow.com
 900×1200 depreciation schedule examples from www.examples.com
900×1200 depreciation schedule examples from www.examples.com
 920×930 les depreciations digischool from www.digischool.fr
920×930 les depreciations digischool from www.digischool.fr
 1275×1650 solution straight method depreciation solved problems studypool from www.studypool.com
1275×1650 solution straight method depreciation solved problems studypool from www.studypool.com
 1920×1080 smart ways avoid depreciation tax rental property from andersonadvisors.com
1920×1080 smart ways avoid depreciation tax rental property from andersonadvisors.com
 1200×849 bonus depreciation effects details analysis tax foundation from taxfoundation.org
1200×849 bonus depreciation effects details analysis tax foundation from taxfoundation.org
 1546×1063 amortissement lineaire ce quil faut savoir mihfada from mihfada.com
1546×1063 amortissement lineaire ce quil faut savoir mihfada from mihfada.com
 886×513 depreciation method tools terry maurer blog from storage.googleapis.com
886×513 depreciation method tools terry maurer blog from storage.googleapis.com
 441×283 depreciation summary forum manage from www.12manage.com
441×283 depreciation summary forum manage from www.12manage.com
 3021×1608 defining calculating written method from khatabook.com
3021×1608 defining calculating written method from khatabook.com
 1920×1536 amortization depreciation methods calculating from www.vecteezy.com
1920×1536 amortization depreciation methods calculating from www.vecteezy.com